Modern web applications built with React and Angular are dynamic, component-driven, and highly interactive. While automated testing plays a crucial role in ensuring stability and regression safety, it often falls short in uncovering unexpected behaviors, usability gaps, and real-world edge cases.
This is where Exploratory Testing becomes invaluable.
Exploratory testing complements automation by empowering testers to think critically, adapt quickly, and uncover risks that scripted tests may overlook—especially in fast-evolving frontend frameworks like React and Angular.
Why Exploratory Testing Matters for React & Angular Applications
React and Angular apps are not static. They involve:
Complex state management
Dynamic UI rendering
Asynchronous API interactions
Frequent UI updates and refactoring
Automated tests verify what we expect, but exploratory testing reveals what we didn’t anticipate.
Key benefits include:
Detecting UI and UX inconsistencies
Identifying state-related issues
Validating real user workflows
Catching framework-specific quirks early
Exploratory testing in React and Angular applications is not about randomness—it’s about guided curiosity, technical awareness, and user empathy. When practiced intentionally, it reveals issues that automation alone cannot detect and strengthens overall product quality.
Exploratory Testing Techniques for Angular Applications
1. Directive and Template Behavior Testing
Angular’s templates, directives, and data bindings are powerful—but complex.
Explore:
Incorrect or delayed bindings
Broken directives under edge conditions
Template errors triggered by unexpected data
2. Dependency Injection & Service Interaction
Angular services often handle core business logic.
Test how the application behaves when:
APIs respond slowly or fail
Services return partial or corrupted data
Multiple services interact simultaneously
These scenarios often reveal hidden stability issues.
3. Routing & Navigation Exploration
Angular routing is robust but can fail in subtle ways.
Explore:
Deep linking
Browser refresh on nested routes
Unauthorized route access
Back/forward navigation behavior
Session-Based Exploratory Testing (SBTM)
To maximize effectiveness, structure your exploratory testing using Session-Based Test Management:
Define a clear mission (e.g., “Explore authentication flows”)
Time-box sessions (60–90 minutes)
Capture observations, bugs, and questions
Review findings with the team
This approach keeps exploratory testing focused yet flexible.
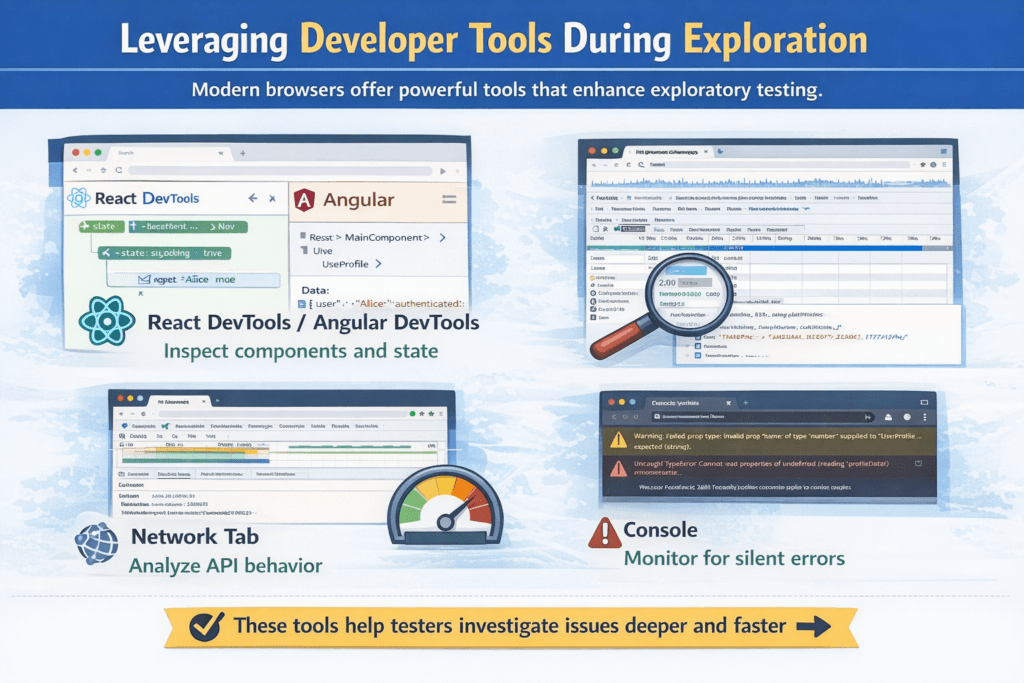
Leveraging Developer Tools During Exploration
Blending Automation with Exploratory Testing
Exploratory testing is not a replacement for automation—it’s a strategic complement.
A balanced testing strategy:
Uses automation for regression and stability
Applies exploratory testing for discovery and risk analysis
Continuously feeds insights from exploration back into automated test coverage
Cross-Browser & Device Behavior Exploration
Browser-Specific UI Anomalies
React and Angular apps may behave differently across browsers and devices.
Exploratory testing should include:
Layout shifts in different browsers
Touch vs. mouse interactions
Mobile-specific navigation patterns
Browser back/forward behavior
These inconsistencies are rarely covered fully by automation.
Data-Driven Exploration
Unusual & Boundary Data Scenarios
Instead of validating expected inputs, explore unexpected data:
Very long strings or special characters
Empty lists, null values, or extreme numbers
Rapid changes in backend data
These scenarios often reveal UI crashes or broken layouts.
Security-Aware Exploratory Testing
Frontend Security Observations
While not a replacement for security testing, exploratory testing can uncover:
Exposure of sensitive data in UI or network calls
Broken authorization flows
Improper handling of session expiration
UI behavior after token tampering or logout
This adds an extra layer of risk awareness.
Collaboration-Driven Exploration
Pair Testing with Developers & Designers
Exploratory testing is more powerful when collaborative.
Try:
Pairing testers with frontend developers
Involving UX designers to validate visual and interaction flows
Conducting group exploratory sessions before releases
This improves shared understanding and faster issue resolution.
Capturing Insights from Exploratory Testing
Turning Discoveries into Long-Term Value
Exploratory testing should feed continuous improvement.
Ensure that:
Critical discoveries become automated test cases
Common failure patterns are documented
UX issues are shared with design teams
Testing charters evolve based on findings
This turns exploration into a strategic asset.
Exploring Error Handling & Resilience
Silent Failures and Graceful Degradation
Many frontend errors never surface as visible failures.
Explore:
How the UI behaves when APIs return empty or partial responses
Whether meaningful error messages are shown to users
If the app recovers gracefully after temporary failures
Exploratory testing helps validate resilience, not just correctness.
Conclusion
As React and Angular applications grow more complex, relying solely on automated checks is no longer enough. Exploratory Testing empowers teams to uncover hidden risks, improve user experience, and build more resilient applications.
By combining structured exploration with strong automation, QA teams can move beyond “does it work?” to confidently answer “does it work well for real users?”
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is exploratory testing still relevant when we have strong automation coverage?
Yes. Automated tests confirm known behaviors, while exploratory testing uncovers unknown risks. Even with high automation coverage, exploratory testing helps identify usability issues, visual defects, performance bottlenecks, and edge cases that scripted tests often miss.
2. How is exploratory testing different from ad-hoc testing?
Exploratory testing is structured and goal-driven, whereas ad-hoc testing is unplanned. Exploratory testing follows clear charters, time-boxed sessions, and documented outcomes, making it a disciplined and repeatable practice.
3. When should exploratory testing be performed in React and Angular projects?
Exploratory testing is most effective:
During early UI development
After major feature changes
Before release cycles
When introducing new frameworks, libraries, or design changes
It fits well into Agile and CI/CD pipelines.
4. Who should perform exploratory testing?
While QA engineers often lead exploratory testing, the best results come from cross-functional collaboration:
Testers bring risk-based thinking
Developers understand technical behavior
Designers validate user experience
Anyone with product knowledge can contribute valuable insights.
Search
Categories

Author
-
Sakthi Raghavi G is a QA Engineer with nearly 2 years of experience in software testing. Over the past year, she has gained hands-on experience in Manual Testing and has also developed a foundational understanding of Automation Testing. She is passionate about continuous learning and consistently takes ownership to drive tasks to completion. Even under high-pressure situations, she maintains focus and productivity often with the help of her favorite playlist. Outside of work, Sakthi enjoys exploring new experiences and staying active by playing badminton.
